Select the correct statement about cardiac output. – Delving into the intricacies of cardiac output, this exploration unravels the fundamental principles governing the cardiovascular system’s vital functions. Cardiac output, a pivotal metric, quantifies the heart’s pumping prowess, providing a window into overall cardiovascular health.
This comprehensive analysis dissects the factors that modulate cardiac output, including heart rate, stroke volume, preload, and afterload. It further delves into the intricate regulatory mechanisms orchestrated by the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and the Frank-Starling law.
Definition of Cardiac Output
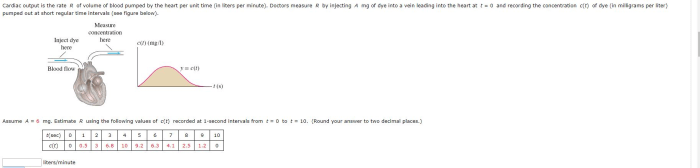
Cardiac output is a fundamental metric in cardiovascular physiology, representing the volume of blood pumped by the heart per unit of time. It is a crucial determinant of tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery throughout the body, playing a pivotal role in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis.
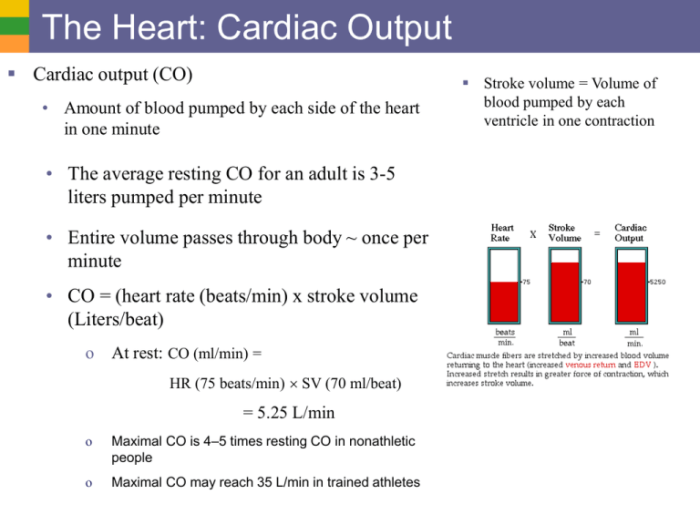
Cardiac output is typically measured in liters per minute (L/min) and is calculated as the product of heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV):
CO = HR x SV
Factors Affecting Cardiac Output
Cardiac output is influenced by a multitude of factors, including:
- Heart rate:The number of heartbeats per minute directly affects cardiac output. Increased heart rate leads to higher cardiac output, while decreased heart rate results in lower cardiac output.
- Stroke volume:The volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle during each heartbeat is a major determinant of cardiac output. Increased stroke volume, such as in athletes, leads to higher cardiac output, while decreased stroke volume, as in heart failure, results in lower cardiac output.
- Preload:The end-diastolic volume (EDV) of the ventricles, or the volume of blood present in the ventricles at the end of diastole, influences stroke volume and thus cardiac output. Increased preload, such as in volume overload, leads to increased stroke volume and cardiac output.
Conversely, decreased preload, as in hypovolemia, results in decreased stroke volume and cardiac output.
- Afterload:The resistance against which the ventricles must pump blood during systole, known as afterload, also affects stroke volume and cardiac output. Increased afterload, such as in hypertension, leads to decreased stroke volume and cardiac output. Conversely, decreased afterload, as in vasodilation, results in increased stroke volume and cardiac output.
Regulation of Cardiac Output

Cardiac output is regulated by a complex interplay of intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, including:
- Autonomic nervous system:The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and stroke volume, leading to increased cardiac output, while the parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart rate, resulting in decreased cardiac output.
- Hormones:Hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine can increase heart rate and stroke volume, leading to increased cardiac output. Conversely, hormones like acetylcholine can decrease heart rate, resulting in decreased cardiac output.
- Frank-Starling law:This principle states that the heart’s stroke volume increases in response to increased preload, up to a limit. This mechanism helps maintain cardiac output in the face of changes in preload.
Clinical Significance of Cardiac Output
Cardiac output is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health. Alterations in cardiac output can signal various cardiovascular conditions, including:
- Increased cardiac output:Can occur in conditions such as hyperthyroidism, anemia, and pregnancy.
- Decreased cardiac output:Can occur in conditions such as heart failure, shock, and hypovolemia.
Cardiac output is commonly measured in clinical practice to assess cardiovascular function and guide therapeutic interventions.
Measurement of Cardiac Output
Various methods are employed to measure cardiac output, each with its advantages and limitations:
- Fick method:This indirect method measures cardiac output by determining the oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
- Thermodilution method:This technique involves injecting a cold solution into the pulmonary artery and measuring the temperature change in the pulmonary vein to calculate cardiac output.
- Doppler echocardiography:This non-invasive method uses ultrasound to measure blood flow velocity in the aorta or pulmonary artery to estimate cardiac output.
User Queries: Select The Correct Statement About Cardiac Output.
What is the significance of cardiac output in assessing cardiovascular health?
Cardiac output provides a quantitative measure of the heart’s pumping efficiency, reflecting the overall health of the cardiovascular system. Alterations in cardiac output can indicate conditions such as heart failure, valvular disorders, and arrhythmias.
How is cardiac output regulated?
Cardiac output is regulated by a complex interplay of mechanisms, including the autonomic nervous system, hormones (e.g., epinephrine, norepinephrine), and the Frank-Starling law, which governs the heart’s ability to adapt to changes in blood volume.
What are the clinical applications of cardiac output measurement?
Cardiac output measurement finds applications in diagnosing and managing cardiovascular conditions, guiding therapeutic interventions, assessing the effectiveness of treatments, and evaluating the prognosis of patients with heart disease.